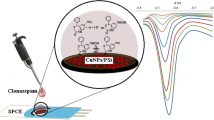
Abstract
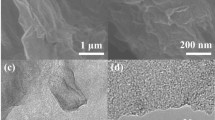
The electrochemical behavior of the anti-inflammatory drug piroxicam is studied at the surface of a plain pyrolytic graphite electrode modified with chitosan-doped carbon nanoparticles. An electroactive surface was produced by drop-casting a suspension of the modifier and characterized by atomic force microscopy. A remarkable enhancement is found in studies on the cyclic voltammetric response towards piroxicam. This is described on the basis of the thin-layer mass transport regimes within the porous films, which leads to a considerable increase in the active surface area of the electrode. The electrode shows a linear response to piroxicam in the range of 0.05–50 μM, with a detection limit of 25 nM (at S/N of 3). The electrode was successfully applied to the determination of piroxicam in pharmaceutical and clinical preparations with satisfactory accuracy and precision.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee R, Chakraborty H, Sarkar M (2003) Photophysical studies of oxicam group of NSAIDs: piroxicam, meloxicam and tenoxicam. Spectrochim Acta Part A 59:1213–1222
Paulus HE, Furst DE, Dromgoole SH (1987) Drugs for rheumatic disease. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 389–398
Sherman KE, Jones C (1992) Hepatotoxicity associated with piroxicam use. Gastroenterology 103:354–355
Abdollahi H, Sororaddin MH, Naseri A (2006) Simultaneous spectrofluorometric determination of piroxicam and pyridoxine using generalized rank annihilation method. Anal Sci 22:263–267
Amin AS (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of piroxicam and tenoxicam in pharmaceutical formulations using alizarin. J Pharm Biomed Anal 29:729–736
Barary MH, Abdel-Hay MH, Sabry SM, Belal TS (2004) Spectrofluorimetric determination of 2-aminopyridine as a potential impurity in piroxicam and tenoxicam within the pharmacopoeial limit. J Pharm Biomed Anal 34:221–226
Basan H, Goger NG, Ertas N, Orbey MT (2001) Quantitative determination of piroxicam in a new formulation (piroxicam-β-cyclodextrin) by derivative UV spectrophotometric method and HPLC. J Pharm Biomed Anal 26:171–178
El-Ries MA, Mohamed G, Khalil S, El-Shall M (2003) Spectrophotometric and potentiometric determination of piroxicam and tenoxicam in pharmaceutical preparations. Chem Pharm Bull 51(1):6–10
Escandar GM, Bystol AJ, Campiglia AD (2002) Spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of piroxicam and pyridoxine. Anal Chim Acta 466:275–283
Bartsch H, Eiper A, Kopelent-Franf HJ (1999) Stability indicating assays for the determination of piroxicam-comparison of methods. J Pharm Biomed Anal 20:531–541
European Pharmacopoeia Council of Europe (2004) 5th ed., Strasbourg, France
Boneschans B, Wessels A, Staden JV, Zovko M, Zorc B, Bergh J (2003) Piroxicam benzoate synthesis, HPLC determination and hydrolysis. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 29:155–160
Gaudiano MC, Valvo L, Bertocchi P, Manna L (2003) RP-HPLC study of the degradation of diclofenac and piroxicam in the presence of hydroxyl radicals. J Pharm Biomed Anal 32:151–158
Ji HY, Lee HW, Kim YH, Jeong DW, Lee HS (2005) Simultaneous determination of piroxicam, meloxicam and tenoxicam in human plasma by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 826:214–219
Al-Kindy SMZ, Al-Wishahi V, Suliman FEO (2004) A sequential injection method for the determination of piroxicam in pharmaceutical formulations using europium sensitized fluorescence. Talanta 64:1343–1350
Chen ZL, Wu SM (2005) Capillary zone electrophoresis for simultaneous determination of seven nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in pharmaceuticals. Anal Bioanal Chem 381:907–912
Acunã JA, de la Fuente C, Vázquez MD, Tascón ML, Gómez MI, Mata F, Sánchez-Batanero P (2002) Electrochemical behaviour of droxicam: kinetic study in aqueous-organic media. J Pharm Biomed Anal 29:617–624
Torriero AAJ, Tonn CE, Sereno L, Raba J (2006) Electrooxidation mechanism of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug piroxicam at glassy carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem 588:218–225
Abbaspour A, Mirzajani R (2007) Electrochemical monitoring of piroxicam in different pharmaceutical forms with multi-walled carbon nanotubes paste electrode. J Pharm Biomed Anal 44:41–48
Kauffmann JM, Vire JC, Gelbche M, Patriarche GJ (1984) Identification des produits de la reduction electrochimique d’un nouvel antiinflammatoire: le piroxicam. Anal Lett 17:2319–2331
Vire JC, Kauffmann JM, Braun J, Patriarche GJ (1985) Caractéristiques électrochimiques d’un nouvel antiinflam-matoire non-stéroidien: le piroxicam. Analusis 13:134–140
Shahrokhian S, Amiri M (2007) Multi-walled carbon nanotube paste electrode for selective voltammetric detection of isoniazid. Microchim Acta 157:149–158
Fang B, Shen R, Zhang W, Wang G, Zhang C (2009) Electrocatalytic oxidation of hydrazine at a chromium hexacyanoferrate/single-walled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 165:231–236
Zhang K, Zhang Y (2010) Electrochemical behavior of adriamycin at an electrode modified with silver nanoparticles and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, and its application. Microchim Acta: published online
Wang C, Wang G, Fang B (2008) Electrocatalytic oxidation of bilirubin at ferrocenecarboxamide modified MWCNT—gold nanocomposite electrodes. Microchim Acta 164:113–118
Streeter I, Wildgoose GG, Shao L, Compton RG (2008) Cyclic voltammetry on electrode surfaces covered with porous layers: an analysis of electron transfer kinetics at single-walled carbon nanotube modified electrodes. Sens Actuators B 133:462–466
Xiao L, Wildgoose GG, Compton RG (2009) Exploring the origins of the apparent “electrocatalysis” observed at C60 film-modified electrodes. Sens Actuators B 138:524–531
Takács-Novák K, Tam KY (2000) Multiwavelength spectrophotometric determination of acid dissociation constants Part V. Tautomerization microcontstants. J Pharm Biomed Anal 21:1171–1182
Ghalkhani M, Shahrokhian S (2010) Application of carbon nanoparticle/chitosan modified electrode for the square-wave adsorptive anodic striping voltammetric determination of Niclosamide. Electrochem Commun 12:66–69
Amiri M, Shahrokhian S, Psillakis E, Marken F (2007) Electrostatic accumulation and determination of triclosan in ultrathin carbon nanoparticle composite film electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 593:117–122
Shahrokhian S, Ghalkhani M (2010) Glassy carbon electrodes modified with a film of nanodiamond—graphite/chitosan: application to the highly sensitive electrochemical determination of Azathioprine. Electrochim Acta 55:3621–3627
Ghorbani-Bidkorbeh F, Shahrokhian S, Mohammadi A, Dinarvand R (2010) Electrochemical determination of naltrexone on the surface of glassy carbon electrode modified with Nafion-doped carbon nanoparticles: application to determinations in pharmaceutical and clinical preparations. J Electroanal Chem 638:212–217
Granger MC, Xu J, Strojek SW, Swain GM (1999) Polycrystalline diamond electrodes: basic properties and applications as amperometric detectors in flow injection analysis and liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 397:145
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Research Council and the Center of Excellence for Nanostructures of the Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran. They are grateful to Professor Mehdi Jalali-Heravi for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahrokhian, S., Jokar, E. & Ghalkhani, M. Electrochemical determination of piroxicam on the surface of pyrolytic graphite electrode modified with a film of carbon nanoparticle-chitosan. Microchim Acta 170, 141–146 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0373-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0373-6